updated docs
This commit is contained in:
635
README.md
635
README.md
@@ -34,8 +34,14 @@ This repository hosts the code of LightRAG. The structure of this code is based
|
||||
<img src="https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/b2aaf634151b4706892693ffb43d9093.png" width="800" alt="LightRAG Diagram">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</br>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<details>
|
||||
<summary style="font-size: 1.4em; font-weight: bold; cursor: pointer; display: list-item;">
|
||||
🎉 News
|
||||
</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
## 🎉 News
|
||||
|
||||
- [x] [2025.02.05]🎯📢Our team has released [VideoRAG](https://github.com/HKUDS/VideoRAG) understanding extremely long-context videos.
|
||||
- [x] [2025.01.13]🎯📢Our team has released [MiniRAG](https://github.com/HKUDS/MiniRAG) making RAG simpler with small models.
|
||||
@@ -54,12 +60,20 @@ This repository hosts the code of LightRAG. The structure of this code is based
|
||||
- [x] [2024.10.16]🎯📢LightRAG now supports [Ollama models](https://github.com/HKUDS/LightRAG?tab=readme-ov-file#quick-start)!
|
||||
- [x] [2024.10.15]🎯📢LightRAG now supports [Hugging Face models](https://github.com/HKUDS/LightRAG?tab=readme-ov-file#quick-start)!
|
||||
|
||||
## Algorithm Flowchart
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
<details>
|
||||
<summary style="font-size: 1.4em; font-weight: bold; cursor: pointer; display: list-item;">
|
||||
Algorithm Flowchart
|
||||
</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
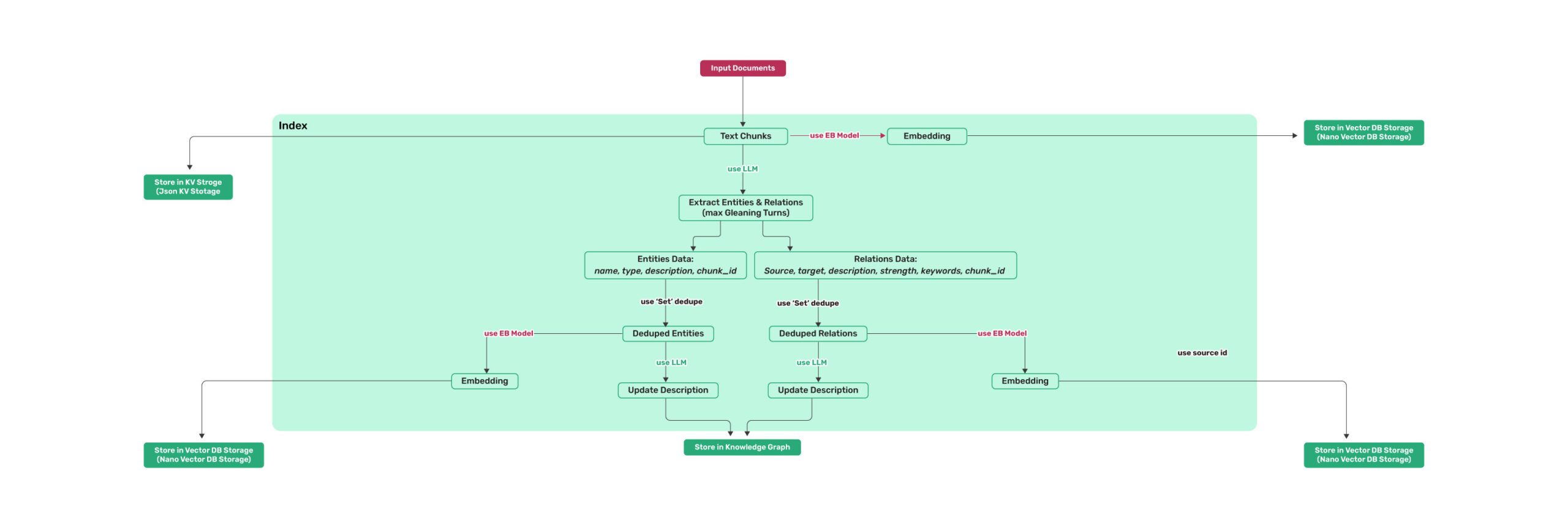
|
||||
*Figure 1: LightRAG Indexing Flowchart - Img Caption : [Source](https://learnopencv.com/lightrag/)*
|
||||
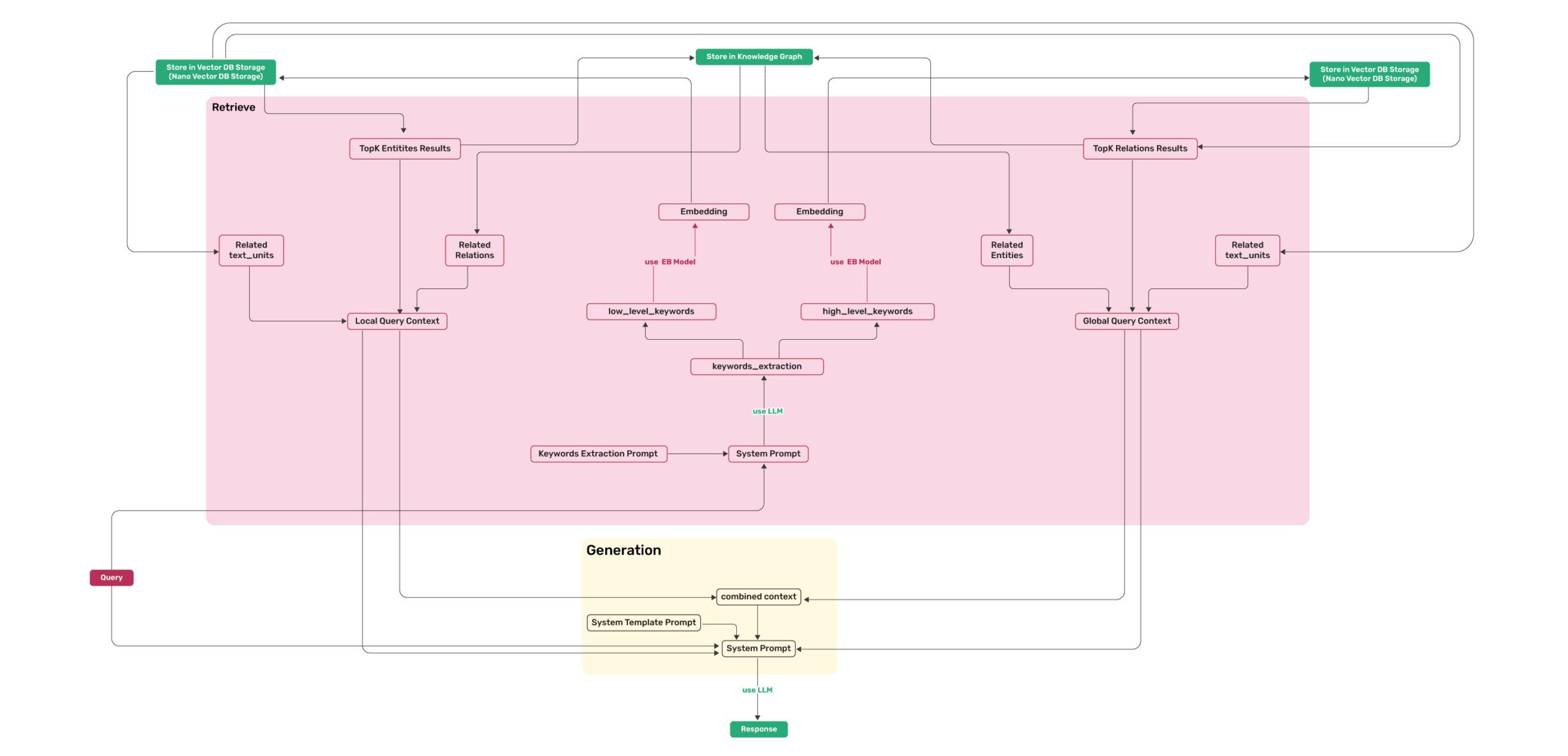
|
||||
*Figure 2: LightRAG Retrieval and Querying Flowchart - Img Caption : [Source](https://learnopencv.com/lightrag/)*
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
## Install
|
||||
|
||||
* Install from source (Recommend)
|
||||
@@ -81,6 +95,9 @@ pip install lightrag-hku
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/gusye1234/nano-graphrag/main/tests/mock_data.txt > ./book.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Query
|
||||
|
||||
Use the below Python snippet (in a script) to initialize LightRAG and perform queries:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
@@ -88,124 +105,67 @@ import os
|
||||
from lightrag import LightRAG, QueryParam
|
||||
from lightrag.llm.openai import gpt_4o_mini_complete, gpt_4o_complete, openai_embed
|
||||
|
||||
#########
|
||||
# Uncomment the below two lines if running in a jupyter notebook to handle the async nature of rag.insert()
|
||||
# import nest_asyncio
|
||||
# nest_asyncio.apply()
|
||||
#########
|
||||
|
||||
WORKING_DIR = "./dickens"
|
||||
|
||||
if not os.path.exists(WORKING_DIR):
|
||||
os.mkdir(WORKING_DIR)
|
||||
|
||||
rag = LightRAG(
|
||||
working_dir=WORKING_DIR,
|
||||
working_dir="your/path",
|
||||
embedding_func=openai_embed,
|
||||
llm_model_func=gpt_4o_mini_complete # Use gpt_4o_mini_complete LLM model
|
||||
# llm_model_func=gpt_4o_complete # Optionally, use a stronger model
|
||||
llm_model_func=gpt_4o_mini_complete
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
with open("./book.txt") as f:
|
||||
rag.insert(f.read())
|
||||
# Insert text
|
||||
rag.insert("Your text")
|
||||
|
||||
# Perform naive search
|
||||
print(rag.query("What are the top themes in this story?", param=QueryParam(mode="naive")))
|
||||
|
||||
mode="naive"
|
||||
# Perform local search
|
||||
print(rag.query("What are the top themes in this story?", param=QueryParam(mode="local")))
|
||||
|
||||
mode="local"
|
||||
# Perform global search
|
||||
print(rag.query("What are the top themes in this story?", param=QueryParam(mode="global")))
|
||||
|
||||
mode="global"
|
||||
# Perform hybrid search
|
||||
print(rag.query("What are the top themes in this story?", param=QueryParam(mode="hybrid")))
|
||||
mode="hybrid"
|
||||
# Mix mode Integrates knowledge graph and vector retrieval.
|
||||
mode="mix"
|
||||
|
||||
# Perform mix search (Knowledge Graph + Vector Retrieval)
|
||||
# Mix mode combines knowledge graph and vector search:
|
||||
# - Uses both structured (KG) and unstructured (vector) information
|
||||
# - Provides comprehensive answers by analyzing relationships and context
|
||||
# - Supports image content through HTML img tags
|
||||
# - Allows control over retrieval depth via top_k parameter
|
||||
print(rag.query("What are the top themes in this story?", param=QueryParam(
|
||||
mode="mix")))
|
||||
rag.query(
|
||||
"What are the top themes in this story?",
|
||||
param=QueryParam(mode=mode)
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Conversation History Support
|
||||
LightRAG now supports multi-turn dialogue through the conversation history feature. Here's how to use it:
|
||||
### Query Param
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from lightrag import LightRAG, QueryParam
|
||||
|
||||
# Initialize LightRAG
|
||||
rag = LightRAG(working_dir=WORKING_DIR)
|
||||
|
||||
# Create conversation history
|
||||
conversation_history = [
|
||||
{"role": "user", "content": "What is the main character's attitude towards Christmas?"},
|
||||
{"role": "assistant", "content": "At the beginning of the story, Ebenezer Scrooge has a very negative attitude towards Christmas..."},
|
||||
{"role": "user", "content": "How does his attitude change?"}
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
# Create query parameters with conversation history
|
||||
query_param = QueryParam(
|
||||
mode="mix", # or any other mode: "local", "global", "hybrid"
|
||||
conversation_history=conversation_history, # Add the conversation history
|
||||
history_turns=3 # Number of recent conversation turns to consider
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Make a query that takes into account the conversation history
|
||||
response = rag.query(
|
||||
"What causes this change in his character?",
|
||||
param=query_param
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Custom Prompt Support
|
||||
LightRAG now supports custom prompts for fine-tuned control over the system's behavior. Here's how to use it:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from lightrag import LightRAG, QueryParam
|
||||
|
||||
# Initialize LightRAG
|
||||
rag = LightRAG(working_dir=WORKING_DIR)
|
||||
|
||||
# Create query parameters
|
||||
query_param = QueryParam(
|
||||
mode="hybrid", # or other mode: "local", "global", "hybrid", "mix" and "naive"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Example 1: Using the default system prompt
|
||||
response_default = rag.query(
|
||||
"What are the primary benefits of renewable energy?",
|
||||
param=query_param
|
||||
)
|
||||
print(response_default)
|
||||
|
||||
# Example 2: Using a custom prompt
|
||||
custom_prompt = """
|
||||
You are an expert assistant in environmental science. Provide detailed and structured answers with examples.
|
||||
---Conversation History---
|
||||
{history}
|
||||
|
||||
---Knowledge Base---
|
||||
{context_data}
|
||||
|
||||
---Response Rules---
|
||||
|
||||
- Target format and length: {response_type}
|
||||
"""
|
||||
response_custom = rag.query(
|
||||
"What are the primary benefits of renewable energy?",
|
||||
param=query_param,
|
||||
system_prompt=custom_prompt # Pass the custom prompt
|
||||
)
|
||||
print(response_custom)
|
||||
class QueryParam:
|
||||
mode: Literal["local", "global", "hybrid", "naive", "mix"] = "global"
|
||||
"""Specifies the retrieval mode:
|
||||
- "local": Focuses on context-dependent information.
|
||||
- "global": Utilizes global knowledge.
|
||||
- "hybrid": Combines local and global retrieval methods.
|
||||
- "naive": Performs a basic search without advanced techniques.
|
||||
- "mix": Integrates knowledge graph and vector retrieval. Mix mode combines knowledge graph and vector search:
|
||||
- Uses both structured (KG) and unstructured (vector) information
|
||||
- Provides comprehensive answers by analyzing relationships and context
|
||||
- Supports image content through HTML img tags
|
||||
- Allows control over retrieval depth via top_k parameter
|
||||
"""
|
||||
only_need_context: bool = False
|
||||
"""If True, only returns the retrieved context without generating a response."""
|
||||
response_type: str = "Multiple Paragraphs"
|
||||
"""Defines the response format. Examples: 'Multiple Paragraphs', 'Single Paragraph', 'Bullet Points'."""
|
||||
top_k: int = 60
|
||||
"""Number of top items to retrieve. Represents entities in 'local' mode and relationships in 'global' mode."""
|
||||
max_token_for_text_unit: int = 4000
|
||||
"""Maximum number of tokens allowed for each retrieved text chunk."""
|
||||
max_token_for_global_context: int = 4000
|
||||
"""Maximum number of tokens allocated for relationship descriptions in global retrieval."""
|
||||
max_token_for_local_context: int = 4000
|
||||
"""Maximum number of tokens allocated for entity descriptions in local retrieval."""
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> default value of Top_k can be change by environment variables TOP_K.
|
||||
|
||||
<details>
|
||||
<summary> Using Open AI-like APIs </summary>
|
||||
<summary> <b>Using Open AI-like APIs</b> </summary>
|
||||
|
||||
* LightRAG also supports Open AI-like chat/embeddings APIs:
|
||||
```python
|
||||
@@ -243,7 +203,7 @@ rag = LightRAG(
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
<details>
|
||||
<summary> Using Hugging Face Models </summary>
|
||||
<summary> <b>Using Hugging Face Models</b> </summary>
|
||||
|
||||
* If you want to use Hugging Face models, you only need to set LightRAG as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -274,7 +234,7 @@ rag = LightRAG(
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
<details>
|
||||
<summary> Using Ollama Models </summary>
|
||||
<summary> <b>Using Ollama Models</b> </summary>
|
||||
|
||||
### Overview
|
||||
If you want to use Ollama models, you need to pull model you plan to use and embedding model, for example `nomic-embed-text`.
|
||||
@@ -353,90 +313,89 @@ In order to run this experiment on low RAM GPU you should select small model and
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
### Query Param
|
||||
<details>
|
||||
<summary> <b>Conversation History Support</b> </summary>
|
||||
|
||||
LightRAG now supports multi-turn dialogue through the conversation history feature. Here's how to use it:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
class QueryParam:
|
||||
mode: Literal["local", "global", "hybrid", "naive", "mix"] = "global"
|
||||
"""Specifies the retrieval mode:
|
||||
- "local": Focuses on context-dependent information.
|
||||
- "global": Utilizes global knowledge.
|
||||
- "hybrid": Combines local and global retrieval methods.
|
||||
- "naive": Performs a basic search without advanced techniques.
|
||||
- "mix": Integrates knowledge graph and vector retrieval.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
only_need_context: bool = False
|
||||
"""If True, only returns the retrieved context without generating a response."""
|
||||
response_type: str = "Multiple Paragraphs"
|
||||
"""Defines the response format. Examples: 'Multiple Paragraphs', 'Single Paragraph', 'Bullet Points'."""
|
||||
top_k: int = 60
|
||||
"""Number of top items to retrieve. Represents entities in 'local' mode and relationships in 'global' mode."""
|
||||
max_token_for_text_unit: int = 4000
|
||||
"""Maximum number of tokens allowed for each retrieved text chunk."""
|
||||
max_token_for_global_context: int = 4000
|
||||
"""Maximum number of tokens allocated for relationship descriptions in global retrieval."""
|
||||
max_token_for_local_context: int = 4000
|
||||
"""Maximum number of tokens allocated for entity descriptions in local retrieval."""
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
from lightrag import LightRAG, QueryParam
|
||||
|
||||
> default value of Top_k can be change by environment variables TOP_K.
|
||||
# Initialize LightRAG
|
||||
rag = LightRAG(working_dir=WORKING_DIR)
|
||||
|
||||
### Batch Insert
|
||||
# Create conversation history
|
||||
conversation_history = [
|
||||
{"role": "user", "content": "What is the main character's attitude towards Christmas?"},
|
||||
{"role": "assistant", "content": "At the beginning of the story, Ebenezer Scrooge has a very negative attitude towards Christmas..."},
|
||||
{"role": "user", "content": "How does his attitude change?"}
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# Basic Batch Insert: Insert multiple texts at once
|
||||
rag.insert(["TEXT1", "TEXT2",...])
|
||||
|
||||
# Batch Insert with custom batch size configuration
|
||||
rag = LightRAG(
|
||||
working_dir=WORKING_DIR,
|
||||
addon_params={
|
||||
"insert_batch_size": 20 # Process 20 documents per batch
|
||||
}
|
||||
)
|
||||
rag.insert(["TEXT1", "TEXT2", "TEXT3", ...]) # Documents will be processed in batches of 20
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The `insert_batch_size` parameter in `addon_params` controls how many documents are processed in each batch during insertion. This is useful for:
|
||||
- Managing memory usage with large document collections
|
||||
- Optimizing processing speed
|
||||
- Providing better progress tracking
|
||||
- Default value is 10 if not specified
|
||||
|
||||
### Incremental Insert
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# Incremental Insert: Insert new documents into an existing LightRAG instance
|
||||
rag = LightRAG(
|
||||
working_dir=WORKING_DIR,
|
||||
llm_model_func=llm_model_func,
|
||||
embedding_func=EmbeddingFunc(
|
||||
embedding_dim=embedding_dimension,
|
||||
max_token_size=8192,
|
||||
func=embedding_func,
|
||||
),
|
||||
# Create query parameters with conversation history
|
||||
query_param = QueryParam(
|
||||
mode="mix", # or any other mode: "local", "global", "hybrid"
|
||||
conversation_history=conversation_history, # Add the conversation history
|
||||
history_turns=3 # Number of recent conversation turns to consider
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
with open("./newText.txt") as f:
|
||||
rag.insert(f.read())
|
||||
# Make a query that takes into account the conversation history
|
||||
response = rag.query(
|
||||
"What causes this change in his character?",
|
||||
param=query_param
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Insert using Pipeline
|
||||
The `apipeline_enqueue_documents` and `apipeline_process_enqueue_documents` functions allow you to perform incremental insertion of documents into the graph.
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
This is useful for scenarios where you want to process documents in the background while still allowing the main thread to continue executing.
|
||||
<details>
|
||||
<summary> <b>Custom Prompt Support</b> </summary>
|
||||
|
||||
And using a routine to process news documents.
|
||||
LightRAG now supports custom prompts for fine-tuned control over the system's behavior. Here's how to use it:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
rag = LightRAG(..)
|
||||
await rag.apipeline_enqueue_documents(input)
|
||||
# Your routine in loop
|
||||
await rag.apipeline_process_enqueue_documents(input)
|
||||
from lightrag import LightRAG, QueryParam
|
||||
|
||||
# Initialize LightRAG
|
||||
rag = LightRAG(working_dir=WORKING_DIR)
|
||||
|
||||
# Create query parameters
|
||||
query_param = QueryParam(
|
||||
mode="hybrid", # or other mode: "local", "global", "hybrid", "mix" and "naive"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Example 1: Using the default system prompt
|
||||
response_default = rag.query(
|
||||
"What are the primary benefits of renewable energy?",
|
||||
param=query_param
|
||||
)
|
||||
print(response_default)
|
||||
|
||||
# Example 2: Using a custom prompt
|
||||
custom_prompt = """
|
||||
You are an expert assistant in environmental science. Provide detailed and structured answers with examples.
|
||||
---Conversation History---
|
||||
{history}
|
||||
|
||||
---Knowledge Base---
|
||||
{context_data}
|
||||
|
||||
---Response Rules---
|
||||
|
||||
- Target format and length: {response_type}
|
||||
"""
|
||||
response_custom = rag.query(
|
||||
"What are the primary benefits of renewable energy?",
|
||||
param=query_param,
|
||||
system_prompt=custom_prompt # Pass the custom prompt
|
||||
)
|
||||
print(response_custom)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Separate Keyword Extraction
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
<details>
|
||||
<summary> <b>Separate Keyword Extraction</b> </summary>
|
||||
|
||||
We've introduced a new function `query_with_separate_keyword_extraction` to enhance the keyword extraction capabilities. This function separates the keyword extraction process from the user's prompt, focusing solely on the query to improve the relevance of extracted keywords.
|
||||
|
||||
##### How It Works?
|
||||
@@ -457,110 +416,10 @@ rag.query_with_separate_keyword_extraction(
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Using Neo4J for Storage
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
* For production level scenarios you will most likely want to leverage an enterprise solution
|
||||
* for KG storage. Running Neo4J in Docker is recommended for seamless local testing.
|
||||
* See: https://hub.docker.com/_/neo4j
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
export NEO4J_URI="neo4j://localhost:7687"
|
||||
export NEO4J_USERNAME="neo4j"
|
||||
export NEO4J_PASSWORD="password"
|
||||
|
||||
# When you launch the project be sure to override the default KG: NetworkX
|
||||
# by specifying kg="Neo4JStorage".
|
||||
|
||||
# Note: Default settings use NetworkX
|
||||
# Initialize LightRAG with Neo4J implementation.
|
||||
WORKING_DIR = "./local_neo4jWorkDir"
|
||||
|
||||
rag = LightRAG(
|
||||
working_dir=WORKING_DIR,
|
||||
llm_model_func=gpt_4o_mini_complete, # Use gpt_4o_mini_complete LLM model
|
||||
graph_storage="Neo4JStorage", #<-----------override KG default
|
||||
log_level="DEBUG" #<-----------override log_level default
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
see test_neo4j.py for a working example.
|
||||
|
||||
### Using PostgreSQL for Storage
|
||||
For production level scenarios you will most likely want to leverage an enterprise solution. PostgreSQL can provide a one-stop solution for you as KV store, VectorDB (pgvector) and GraphDB (apache AGE).
|
||||
* PostgreSQL is lightweight,the whole binary distribution including all necessary plugins can be zipped to 40MB: Ref to [Windows Release](https://github.com/ShanGor/apache-age-windows/releases/tag/PG17%2Fv1.5.0-rc0) as it is easy to install for Linux/Mac.
|
||||
* If you prefer docker, please start with this image if you are a beginner to avoid hiccups (DO read the overview): https://hub.docker.com/r/shangor/postgres-for-rag
|
||||
* How to start? Ref to: [examples/lightrag_zhipu_postgres_demo.py](https://github.com/HKUDS/LightRAG/blob/main/examples/lightrag_zhipu_postgres_demo.py)
|
||||
* Create index for AGE example: (Change below `dickens` to your graph name if necessary)
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
load 'age';
|
||||
SET search_path = ag_catalog, "$user", public;
|
||||
CREATE INDEX CONCURRENTLY entity_p_idx ON dickens."Entity" (id);
|
||||
CREATE INDEX CONCURRENTLY vertex_p_idx ON dickens."_ag_label_vertex" (id);
|
||||
CREATE INDEX CONCURRENTLY directed_p_idx ON dickens."DIRECTED" (id);
|
||||
CREATE INDEX CONCURRENTLY directed_eid_idx ON dickens."DIRECTED" (end_id);
|
||||
CREATE INDEX CONCURRENTLY directed_sid_idx ON dickens."DIRECTED" (start_id);
|
||||
CREATE INDEX CONCURRENTLY directed_seid_idx ON dickens."DIRECTED" (start_id,end_id);
|
||||
CREATE INDEX CONCURRENTLY edge_p_idx ON dickens."_ag_label_edge" (id);
|
||||
CREATE INDEX CONCURRENTLY edge_sid_idx ON dickens."_ag_label_edge" (start_id);
|
||||
CREATE INDEX CONCURRENTLY edge_eid_idx ON dickens."_ag_label_edge" (end_id);
|
||||
CREATE INDEX CONCURRENTLY edge_seid_idx ON dickens."_ag_label_edge" (start_id,end_id);
|
||||
create INDEX CONCURRENTLY vertex_idx_node_id ON dickens."_ag_label_vertex" (ag_catalog.agtype_access_operator(properties, '"node_id"'::agtype));
|
||||
create INDEX CONCURRENTLY entity_idx_node_id ON dickens."Entity" (ag_catalog.agtype_access_operator(properties, '"node_id"'::agtype));
|
||||
CREATE INDEX CONCURRENTLY entity_node_id_gin_idx ON dickens."Entity" using gin(properties);
|
||||
ALTER TABLE dickens."DIRECTED" CLUSTER ON directed_sid_idx;
|
||||
|
||||
-- drop if necessary
|
||||
drop INDEX entity_p_idx;
|
||||
drop INDEX vertex_p_idx;
|
||||
drop INDEX directed_p_idx;
|
||||
drop INDEX directed_eid_idx;
|
||||
drop INDEX directed_sid_idx;
|
||||
drop INDEX directed_seid_idx;
|
||||
drop INDEX edge_p_idx;
|
||||
drop INDEX edge_sid_idx;
|
||||
drop INDEX edge_eid_idx;
|
||||
drop INDEX edge_seid_idx;
|
||||
drop INDEX vertex_idx_node_id;
|
||||
drop INDEX entity_idx_node_id;
|
||||
drop INDEX entity_node_id_gin_idx;
|
||||
```
|
||||
* Known issue of the Apache AGE: The released versions got below issue:
|
||||
> You might find that the properties of the nodes/edges are empty.
|
||||
> It is a known issue of the release version: https://github.com/apache/age/pull/1721
|
||||
>
|
||||
> You can Compile the AGE from source code and fix it.
|
||||
|
||||
### Using Faiss for Storage
|
||||
- Install the required dependencies:
|
||||
```
|
||||
pip install faiss-cpu
|
||||
```
|
||||
You can also install `faiss-gpu` if you have GPU support.
|
||||
|
||||
- Here we are using `sentence-transformers` but you can also use `OpenAIEmbedding` model with `3072` dimensions.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
async def embedding_func(texts: list[str]) -> np.ndarray:
|
||||
model = SentenceTransformer('all-MiniLM-L6-v2')
|
||||
embeddings = model.encode(texts, convert_to_numpy=True)
|
||||
return embeddings
|
||||
|
||||
# Initialize LightRAG with the LLM model function and embedding function
|
||||
rag = LightRAG(
|
||||
working_dir=WORKING_DIR,
|
||||
llm_model_func=llm_model_func,
|
||||
embedding_func=EmbeddingFunc(
|
||||
embedding_dim=384,
|
||||
max_token_size=8192,
|
||||
func=embedding_func,
|
||||
),
|
||||
vector_storage="FaissVectorDBStorage",
|
||||
vector_db_storage_cls_kwargs={
|
||||
"cosine_better_than_threshold": 0.3 # Your desired threshold
|
||||
}
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Insert Custom KG
|
||||
<details>
|
||||
<summary> <b>Insert Custom KG</b> </summary>
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
rag = LightRAG(
|
||||
@@ -616,6 +475,213 @@ custom_kg = {
|
||||
|
||||
rag.insert_custom_kg(custom_kg)
|
||||
```
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
## Insert
|
||||
|
||||
#### Basic Insert
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# Basic Insert
|
||||
rag.insert("Text")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<details>
|
||||
<summary> <b> Batch Insert </b></summary>
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# Basic Batch Insert: Insert multiple texts at once
|
||||
rag.insert(["TEXT1", "TEXT2",...])
|
||||
|
||||
# Batch Insert with custom batch size configuration
|
||||
rag = LightRAG(
|
||||
working_dir=WORKING_DIR,
|
||||
addon_params={
|
||||
"insert_batch_size": 20 # Process 20 documents per batch
|
||||
}
|
||||
)
|
||||
rag.insert(["TEXT1", "TEXT2", "TEXT3", ...]) # Documents will be processed in batches of 20
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The `insert_batch_size` parameter in `addon_params` controls how many documents are processed in each batch during insertion. This is useful for:
|
||||
- Managing memory usage with large document collections
|
||||
- Optimizing processing speed
|
||||
- Providing better progress tracking
|
||||
- Default value is 10 if not specified
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<details>
|
||||
<summary><b>Incremental Insert</b></summary>
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# Incremental Insert: Insert new documents into an existing LightRAG instance
|
||||
rag = LightRAG(
|
||||
working_dir=WORKING_DIR,
|
||||
llm_model_func=llm_model_func,
|
||||
embedding_func=EmbeddingFunc(
|
||||
embedding_dim=embedding_dimension,
|
||||
max_token_size=8192,
|
||||
func=embedding_func,
|
||||
),
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
with open("./newText.txt") as f:
|
||||
rag.insert(f.read())
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
<details>
|
||||
<summary><b>Insert using Pipeline</b></summary>
|
||||
|
||||
The `apipeline_enqueue_documents` and `apipeline_process_enqueue_documents` functions allow you to perform incremental insertion of documents into the graph.
|
||||
|
||||
This is useful for scenarios where you want to process documents in the background while still allowing the main thread to continue executing.
|
||||
|
||||
And using a routine to process news documents.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
rag = LightRAG(..)
|
||||
await rag.apipeline_enqueue_documents(input)
|
||||
# Your routine in loop
|
||||
await rag.apipeline_process_enqueue_documents(input)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
<details>
|
||||
<summary><b>Insert Multi-file Type Support</b></summary>
|
||||
|
||||
The `textract` supports reading file types such as TXT, DOCX, PPTX, CSV, and PDF.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import textract
|
||||
|
||||
file_path = 'TEXT.pdf'
|
||||
text_content = textract.process(file_path)
|
||||
|
||||
rag.insert(text_content.decode('utf-8'))
|
||||
```
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
### Storage
|
||||
|
||||
<details>
|
||||
<summary> <b>Using Neo4J for Storage</b> </summary>
|
||||
|
||||
* For production level scenarios you will most likely want to leverage an enterprise solution
|
||||
* for KG storage. Running Neo4J in Docker is recommended for seamless local testing.
|
||||
* See: https://hub.docker.com/_/neo4j
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
export NEO4J_URI="neo4j://localhost:7687"
|
||||
export NEO4J_USERNAME="neo4j"
|
||||
export NEO4J_PASSWORD="password"
|
||||
|
||||
# When you launch the project be sure to override the default KG: NetworkX
|
||||
# by specifying kg="Neo4JStorage".
|
||||
|
||||
# Note: Default settings use NetworkX
|
||||
# Initialize LightRAG with Neo4J implementation.
|
||||
WORKING_DIR = "./local_neo4jWorkDir"
|
||||
|
||||
rag = LightRAG(
|
||||
working_dir=WORKING_DIR,
|
||||
llm_model_func=gpt_4o_mini_complete, # Use gpt_4o_mini_complete LLM model
|
||||
graph_storage="Neo4JStorage", #<-----------override KG default
|
||||
log_level="DEBUG" #<-----------override log_level default
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
see test_neo4j.py for a working example.
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
<details>
|
||||
<summary> <b>Using PostgreSQL for Storage</b> </summary>
|
||||
|
||||
For production level scenarios you will most likely want to leverage an enterprise solution. PostgreSQL can provide a one-stop solution for you as KV store, VectorDB (pgvector) and GraphDB (apache AGE).
|
||||
* PostgreSQL is lightweight,the whole binary distribution including all necessary plugins can be zipped to 40MB: Ref to [Windows Release](https://github.com/ShanGor/apache-age-windows/releases/tag/PG17%2Fv1.5.0-rc0) as it is easy to install for Linux/Mac.
|
||||
* If you prefer docker, please start with this image if you are a beginner to avoid hiccups (DO read the overview): https://hub.docker.com/r/shangor/postgres-for-rag
|
||||
* How to start? Ref to: [examples/lightrag_zhipu_postgres_demo.py](https://github.com/HKUDS/LightRAG/blob/main/examples/lightrag_zhipu_postgres_demo.py)
|
||||
* Create index for AGE example: (Change below `dickens` to your graph name if necessary)
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
load 'age';
|
||||
SET search_path = ag_catalog, "$user", public;
|
||||
CREATE INDEX CONCURRENTLY entity_p_idx ON dickens."Entity" (id);
|
||||
CREATE INDEX CONCURRENTLY vertex_p_idx ON dickens."_ag_label_vertex" (id);
|
||||
CREATE INDEX CONCURRENTLY directed_p_idx ON dickens."DIRECTED" (id);
|
||||
CREATE INDEX CONCURRENTLY directed_eid_idx ON dickens."DIRECTED" (end_id);
|
||||
CREATE INDEX CONCURRENTLY directed_sid_idx ON dickens."DIRECTED" (start_id);
|
||||
CREATE INDEX CONCURRENTLY directed_seid_idx ON dickens."DIRECTED" (start_id,end_id);
|
||||
CREATE INDEX CONCURRENTLY edge_p_idx ON dickens."_ag_label_edge" (id);
|
||||
CREATE INDEX CONCURRENTLY edge_sid_idx ON dickens."_ag_label_edge" (start_id);
|
||||
CREATE INDEX CONCURRENTLY edge_eid_idx ON dickens."_ag_label_edge" (end_id);
|
||||
CREATE INDEX CONCURRENTLY edge_seid_idx ON dickens."_ag_label_edge" (start_id,end_id);
|
||||
create INDEX CONCURRENTLY vertex_idx_node_id ON dickens."_ag_label_vertex" (ag_catalog.agtype_access_operator(properties, '"node_id"'::agtype));
|
||||
create INDEX CONCURRENTLY entity_idx_node_id ON dickens."Entity" (ag_catalog.agtype_access_operator(properties, '"node_id"'::agtype));
|
||||
CREATE INDEX CONCURRENTLY entity_node_id_gin_idx ON dickens."Entity" using gin(properties);
|
||||
ALTER TABLE dickens."DIRECTED" CLUSTER ON directed_sid_idx;
|
||||
|
||||
-- drop if necessary
|
||||
drop INDEX entity_p_idx;
|
||||
drop INDEX vertex_p_idx;
|
||||
drop INDEX directed_p_idx;
|
||||
drop INDEX directed_eid_idx;
|
||||
drop INDEX directed_sid_idx;
|
||||
drop INDEX directed_seid_idx;
|
||||
drop INDEX edge_p_idx;
|
||||
drop INDEX edge_sid_idx;
|
||||
drop INDEX edge_eid_idx;
|
||||
drop INDEX edge_seid_idx;
|
||||
drop INDEX vertex_idx_node_id;
|
||||
drop INDEX entity_idx_node_id;
|
||||
drop INDEX entity_node_id_gin_idx;
|
||||
```
|
||||
* Known issue of the Apache AGE: The released versions got below issue:
|
||||
> You might find that the properties of the nodes/edges are empty.
|
||||
> It is a known issue of the release version: https://github.com/apache/age/pull/1721
|
||||
>
|
||||
> You can Compile the AGE from source code and fix it.
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
<details>
|
||||
<summary> <b>Using Faiss for Storage</b> </summary>
|
||||
|
||||
- Install the required dependencies:
|
||||
```
|
||||
pip install faiss-cpu
|
||||
```
|
||||
You can also install `faiss-gpu` if you have GPU support.
|
||||
|
||||
- Here we are using `sentence-transformers` but you can also use `OpenAIEmbedding` model with `3072` dimensions.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
async def embedding_func(texts: list[str]) -> np.ndarray:
|
||||
model = SentenceTransformer('all-MiniLM-L6-v2')
|
||||
embeddings = model.encode(texts, convert_to_numpy=True)
|
||||
return embeddings
|
||||
|
||||
# Initialize LightRAG with the LLM model function and embedding function
|
||||
rag = LightRAG(
|
||||
working_dir=WORKING_DIR,
|
||||
llm_model_func=llm_model_func,
|
||||
embedding_func=EmbeddingFunc(
|
||||
embedding_dim=384,
|
||||
max_token_size=8192,
|
||||
func=embedding_func,
|
||||
),
|
||||
vector_storage="FaissVectorDBStorage",
|
||||
vector_db_storage_cls_kwargs={
|
||||
"cosine_better_than_threshold": 0.3 # Your desired threshold
|
||||
}
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Delete
|
||||
```python
|
||||
@@ -637,18 +703,6 @@ rag.delete_by_entity("Project Gutenberg")
|
||||
rag.delete_by_doc_id("doc_id")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Multi-file Type Support
|
||||
|
||||
The `textract` supports reading file types such as TXT, DOCX, PPTX, CSV, and PDF.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import textract
|
||||
|
||||
file_path = 'TEXT.pdf'
|
||||
text_content = textract.process(file_path)
|
||||
|
||||
rag.insert(text_content.decode('utf-8'))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Graph Visualization
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -806,6 +860,9 @@ if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
|
||||
### LightRAG init parameters
|
||||
|
||||
<details>
|
||||
<summary> Parameters </summary>
|
||||
|
||||
| **Parameter** | **Type** | **Explanation** | **Default** |
|
||||
|----------------------------------------------| --- |-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| **working\_dir** | `str` | Directory where the cache will be stored | `lightrag_cache+timestamp` |
|
||||
@@ -836,6 +893,8 @@ if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
| **embedding\_cache\_config** | `dict` | Configuration for question-answer caching. Contains three parameters:<br>- `enabled`: Boolean value to enable/disable cache lookup functionality. When enabled, the system will check cached responses before generating new answers.<br>- `similarity_threshold`: Float value (0-1), similarity threshold. When a new question's similarity with a cached question exceeds this threshold, the cached answer will be returned directly without calling the LLM.<br>- `use_llm_check`: Boolean value to enable/disable LLM similarity verification. When enabled, LLM will be used as a secondary check to verify the similarity between questions before returning cached answers. | Default: `{"enabled": False, "similarity_threshold": 0.95, "use_llm_check": False}` |
|
||||
|**log\_dir** | `str` | Directory to store logs. | `./` |
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
### Error Handling
|
||||
|
||||
<details>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,12 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# Handy Tips for Developers Who Want to Contribute to the Project
|
||||
## Pre-commit Hooks
|
||||
Please ensure you have run pre-commit hooks before committing your changes.
|
||||
### Guides
|
||||
1. **Installing Pre-commit Hooks**:
|
||||
- Install pre-commit using pip: `pip install pre-commit`
|
||||
- Initialize pre-commit in your repository: `pre-commit install`
|
||||
- Run pre-commit hooks: `pre-commit run --all-files`
|
||||
|
||||
2. **Pre-commit Hooks Configuration**:
|
||||
- Create a `.pre-commit-config.yaml` file in the root of your repository.
|
||||
- Add your hooks to the `.pre-commit-config.yaml`file.
|
||||
Reference in New Issue
Block a user